Are all cryptocurrencies the same
Digital money and the underlying technology, in many cases blockchain, overcome some of the key constraints of today’s payment processes – particularly around speed and availability Welcome bonuses at online casinos. Digital money enables payments to be available 24/7, 365 days without any closing hours. Settlement will be near instant all around the globe and fees for cross-border remittances will be an order of magnitude lower than in today’s world of correspondent banks.
As digital payments continue to evolve, both businesses and consumers must prepare for the changes ahead. For businesses, this means staying agile and adaptable to new payment technologies. Investing in the latest payment infrastructure, such as contactless terminals and mobile payment solutions, will be crucial. Additionally, businesses should consider diversifying their payment options to include cryptocurrencies, catering to a wider range of customers.
Card networks have delivered scale, security and interoperability, but the reality is that merchants bear high costs, and consumers are incentivized with rewards to keep using the same credit-based rails. It’s created a payments environment that is harder to evolve.
Do all cryptocurrencies use blockchain
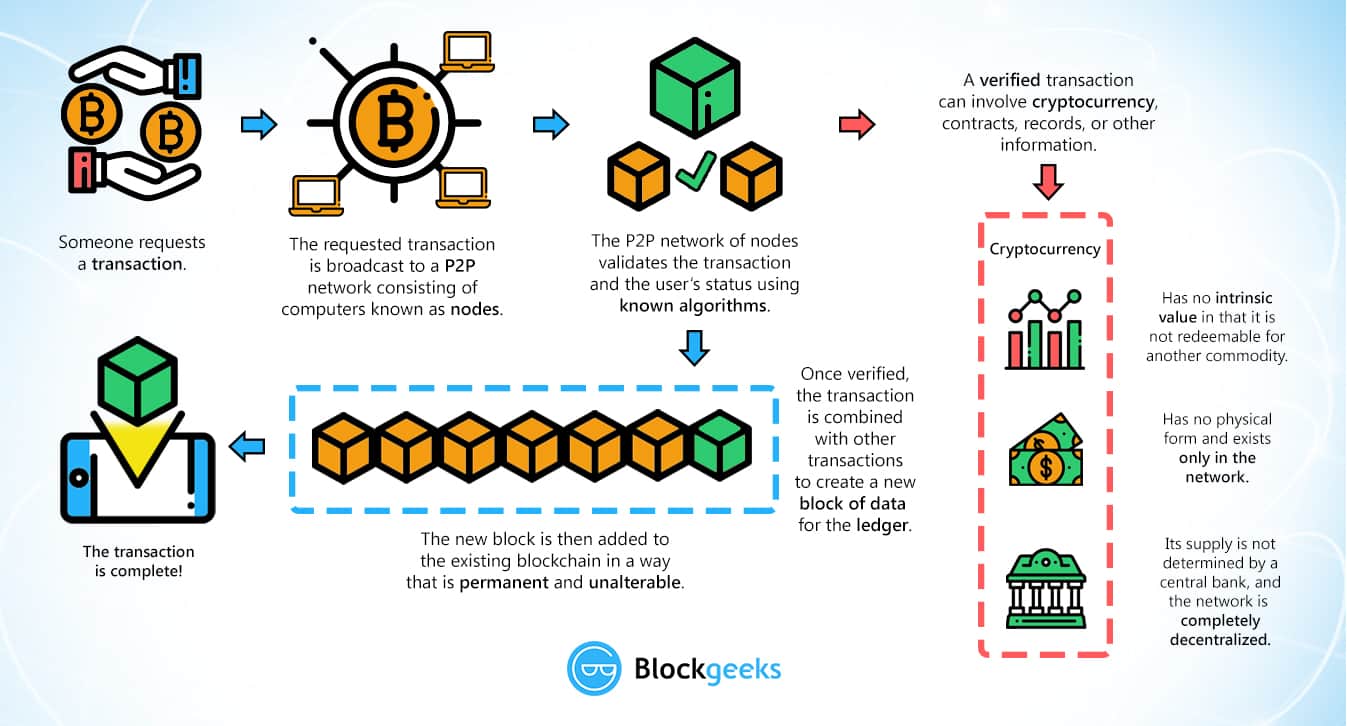
Since blockchains operate 24/7, people can make more efficient financial and asset transfers, especially internationally. They don’t need to wait days for a bank or a government agency to manually confirm everything.
Why are consensus mechanisms pivotal in blockchain networks? Three words: trust, security, and decentralization. These algorithms make sure everyone’s singing from the same hymn sheet, keeping the network transparent and secure. They’re the guardians at the gate, making it costly and complicated for any fraudsters to mess with the blockchain.
“We see great potential in the area of smart contracts—using blockchain technology and coded instructions to automate legal contracts,” says Gray. “A properly coded smart legal contract on a distributed ledger can minimize, or preferably eliminate, the need for outside third parties to verify performance.”
Tokens, by contrast, are created on top of existing blockchains that already have a native currency. Think about bitcoin and ether, for example: they were created on their own native blockchains, Bitcoin and Ethereum, respectively.
There are four main types of blockchain networks: public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains and hybrid blockchains. Each one of these platforms has its benefits, drawbacks and ideal uses.
Why do all cryptocurrencies rise and fall together
In the U.S., discussions about reversing digital asset regulations have caused market volatility. The potential elimination of the IRS’s crypto broker rule has further fueled uncertainty. These examples demonstrate how regulatory decisions can create ripple effects across the cryptocurrency market.
Security breaches can shake investor confidence and cause significant price fluctuations in the cryptocurrency market. When hackers exploit vulnerabilities in blockchain networks or cryptocurrency exchanges, panic often sets in. Investors rush to sell their holdings, leading to sharp declines in price. For example, high-profile breaches like the Mt. Gox hack in 2014 resulted in bitcoin losing over 50% of its value within weeks.
Bitcoin halving reduces the number of new coins miners receive, limiting supply. With demand often staying the same or increasing, prices tend to rise over time. Historically, Bitcoin has seen significant growth 12-18 months after a halving.
So now, if someone asks you what makes crypto go up and down, you have the answers. However, crypto is still volatile and a hugely speculated space. Hence, global regulations, bans, and pro-crypto stances can also impact prices. Due to the plethora of price-influencing factors at play, you should always do your research before making any crypto-specific decision.